Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Upper Limb Anatomy Detailed Explanation Bones Muscles Nerves Joints
Frequently Asked Questions
Upper limb anatomy is the study of the structure of the shoulder arm forearm and hand including bones joints muscles nerves blood vessels and lymphatics responsible for movement sensation and manipulation.
The bones of the upper limb include the clavicle scapula humerus radius ulna eight carpal bones five metacarpals and fourteen phalanges.
The upper limb is divided into the pectoral region axilla arm forearm and hand.
The pectoral girdle connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton and allows a wide range of shoulder movements.
The shoulder joint provides the greatest range of motion due to its ball and socket structure.
The rotator cuff muscles are supraspinatus infraspinatus teres minor and subscapularis.
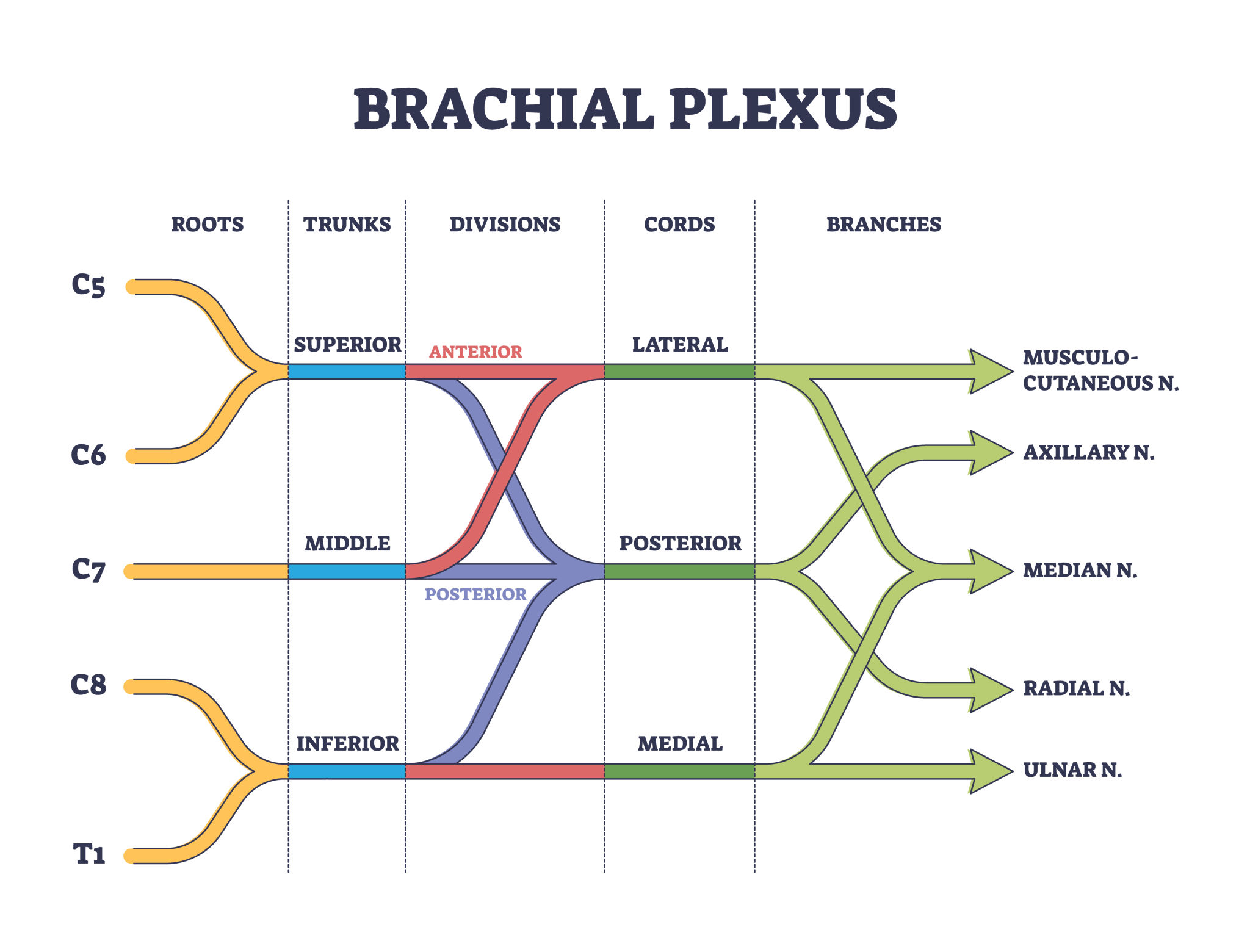
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves formed by spinal nerves C5 to T1 that supplies motor and sensory innervation to the upper limb.
Injury to the radial nerve causes wrist drop due to paralysis of wrist and finger extensors.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is compression of the median nerve beneath the flexor retinaculum causing pain numbness and weakness in the hand.
The subclavian artery continues as the axillary artery and then the brachial artery supplying most of the upper limb.
The anatomical snuffbox is a triangular depression on the lateral wrist containing the radial artery and is clinically important in scaphoid fractures.
The dorsal interossei muscles abduct the fingers while palmar interossei adduct them.
Claw hand deformity is caused by ulnar nerve injury leading to paralysis of intrinsic hand muscles.
Lumbricals flex the metacarpophalangeal joints and extend the interphalangeal joints of the fingers.
The scaphoid has a retrograde blood supply making its proximal part vulnerable to avascular necrosis after fracture.