Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Glands of Head and Neck Anatomy Types Functions and Clinical Importance
Frequently Asked Questions
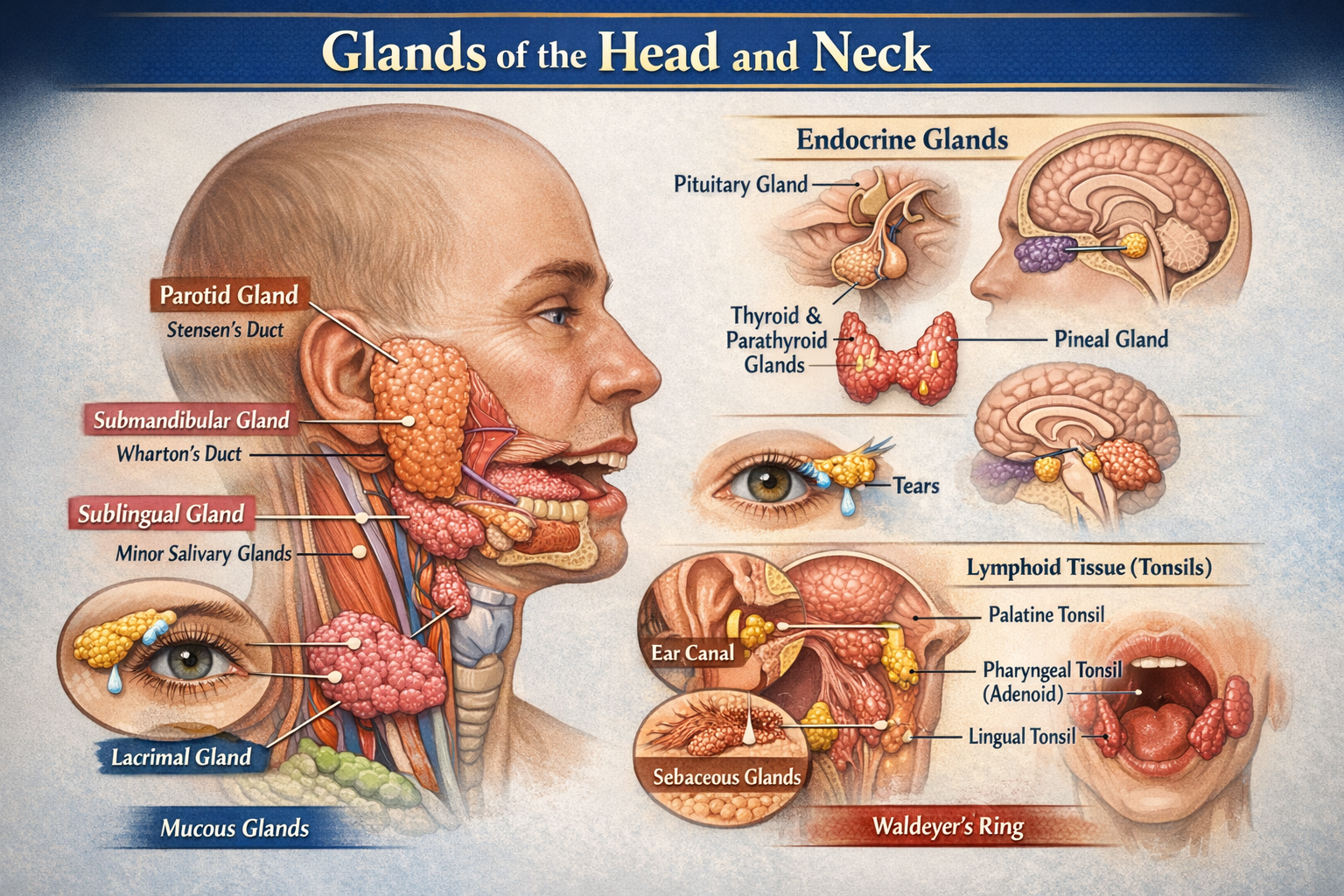
The main glands of the head and neck include the major salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, sublingual), minor salivary glands, endocrine glands (thyroid, parathyroid, pituitary, pineal), lacrimal glands, sebaceous glands, ceruminous glands, and lymphoid glands such as the tonsils.
The parotid gland is the largest salivary gland in the head and neck and is predominantly a serous gland.
The parasympathetic secretomotor supply to the parotid gland is provided by the glossopharyngeal nerve via the lesser petrosal nerve and otic ganglion.
The submandibular gland is most commonly affected by salivary stones due to the long and upward course of Wharton duct and thicker saliva.
The sublingual gland primarily secretes mucous saliva that helps in lubrication of the oral cavity and facilitation of swallowing.
The thyroid gland secretes thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin, which regulate metabolism, growth, and calcium homeostasis.
Hypocalcemia after thyroid surgery occurs due to accidental removal or damage to the parathyroid glands, leading to reduced parathyroid hormone secretion.
The pituitary gland acts as the master endocrine gland by regulating growth, metabolism, reproduction, stress response, and the activity of other endocrine glands.
The pineal gland regulates circadian rhythm by secreting the hormone melatonin.
Ceruminous glands are modified apocrine sweat glands in the external auditory canal that produce cerumen (ear wax) to protect and lubricate the ear canal.
The lacrimal gland produces tears that lubricate the eye, remove debris, and provide antimicrobial protection.
Minor salivary glands are small mucous-secreting glands located in the lips, cheeks, tongue, soft palate, and oropharynx.
Tumors of minor salivary glands are most likely to be malignant compared to major salivary glands.
A ranula is a mucous retention cyst arising from the sublingual gland in the floor of the mouth.
Tonsils are lymphoid glandular structures forming Waldeyer ring and play a role in immune defense by trapping and responding to pathogens entering through the oral and nasal cavities.
MCQ Test - Glands of Head and Neck Anatomy Types Functions and Clinical Importance
No MCQs available for this article.