Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Development of Tongue, Pituitary Gland, Face, Palate and Thyroid – Complete Embryology Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
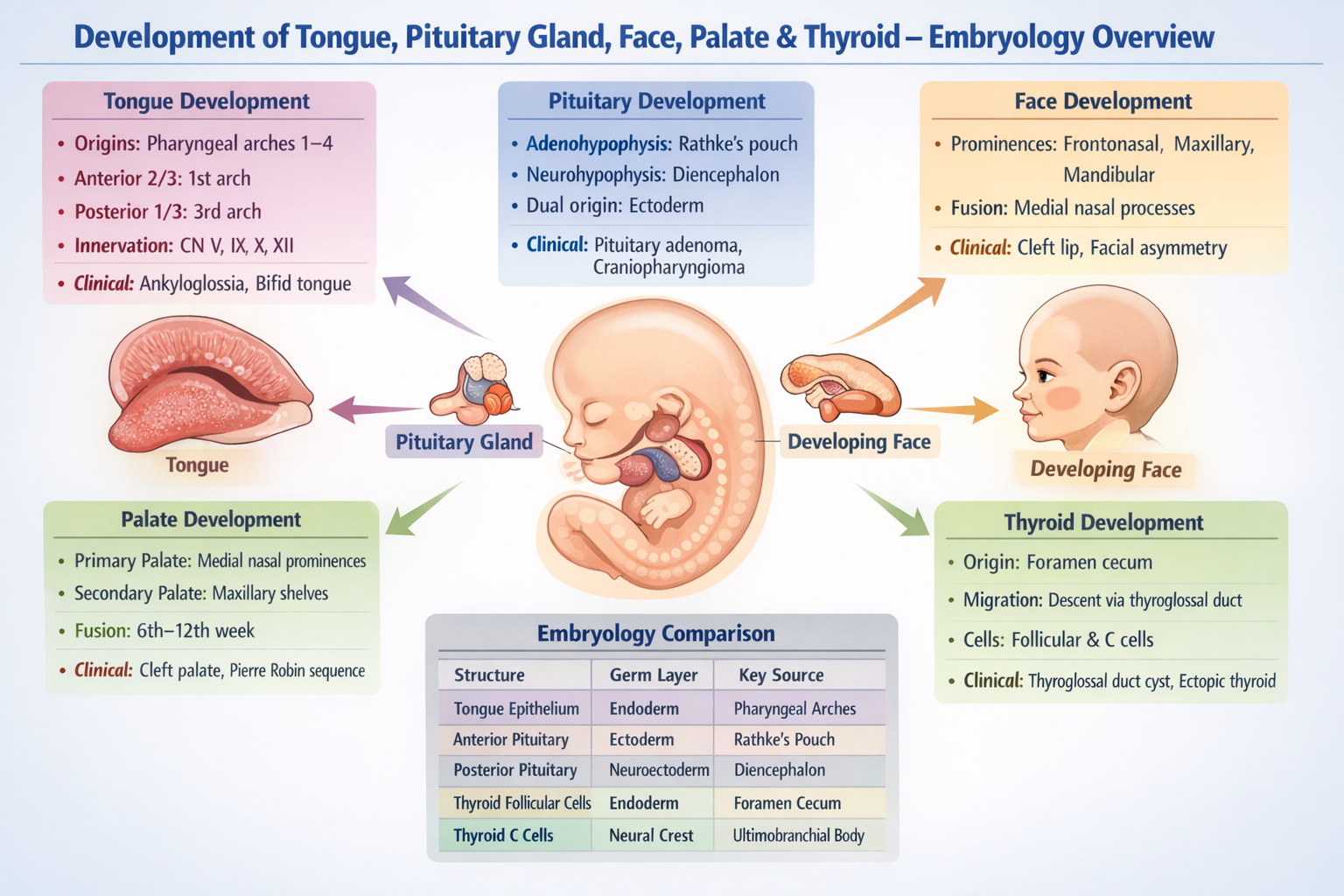
The anterior two thirds of the tongue develop from the first pharyngeal arch through the lateral lingual swellings.
The posterior one third of the tongue develops from the third pharyngeal arch.
Tongue muscles originate from occipital myotomes and are supplied by the hypoglossal nerve.
The pituitary gland has a dual origin: the anterior pituitary develops from Rathke’s pouch (oral ectoderm) and the posterior pituitary develops from neuroectoderm of the diencephalon.
Craniopharyngioma arises from remnants of Rathke’s pouch.
The upper lip is formed by fusion of the maxillary prominences with the medial nasal prominences.
Cleft lip occurs due to failure of fusion between the maxillary prominence and the medial nasal prominence.
The primary palate is formed from the median palatine process derived from the medial nasal prominences.
Cleft palate results from failure of fusion or elevation of the palatine shelves derived from maxillary prominences.
Fusion of the secondary palate is usually completed between the 10th and 12th weeks of gestation.
The thyroid gland originates from endoderm at the foramen cecum on the dorsum of the tongue.
The thyroglossal duct is a transient embryological tract through which the thyroid gland descends from the foramen cecum to its final position in the neck.
A thyroglossal duct cyst results from persistence of the thyroglossal duct after thyroid migration.
Lingual thyroid occurs when the thyroid gland fails to descend and remains at the foramen cecum.
Parafollicular cells originate from neural crest cells via the ultimobranchial body of the fourth pharyngeal pouch.
MCQ Test - Development of Tongue, Pituitary Gland, Face, Palate and Thyroid – Complete Embryology Guide
No MCQs available for this article.