Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Dural Folds and Dural Venous Sinuses Anatomy, Features and Clinical Significance
Frequently Asked Questions
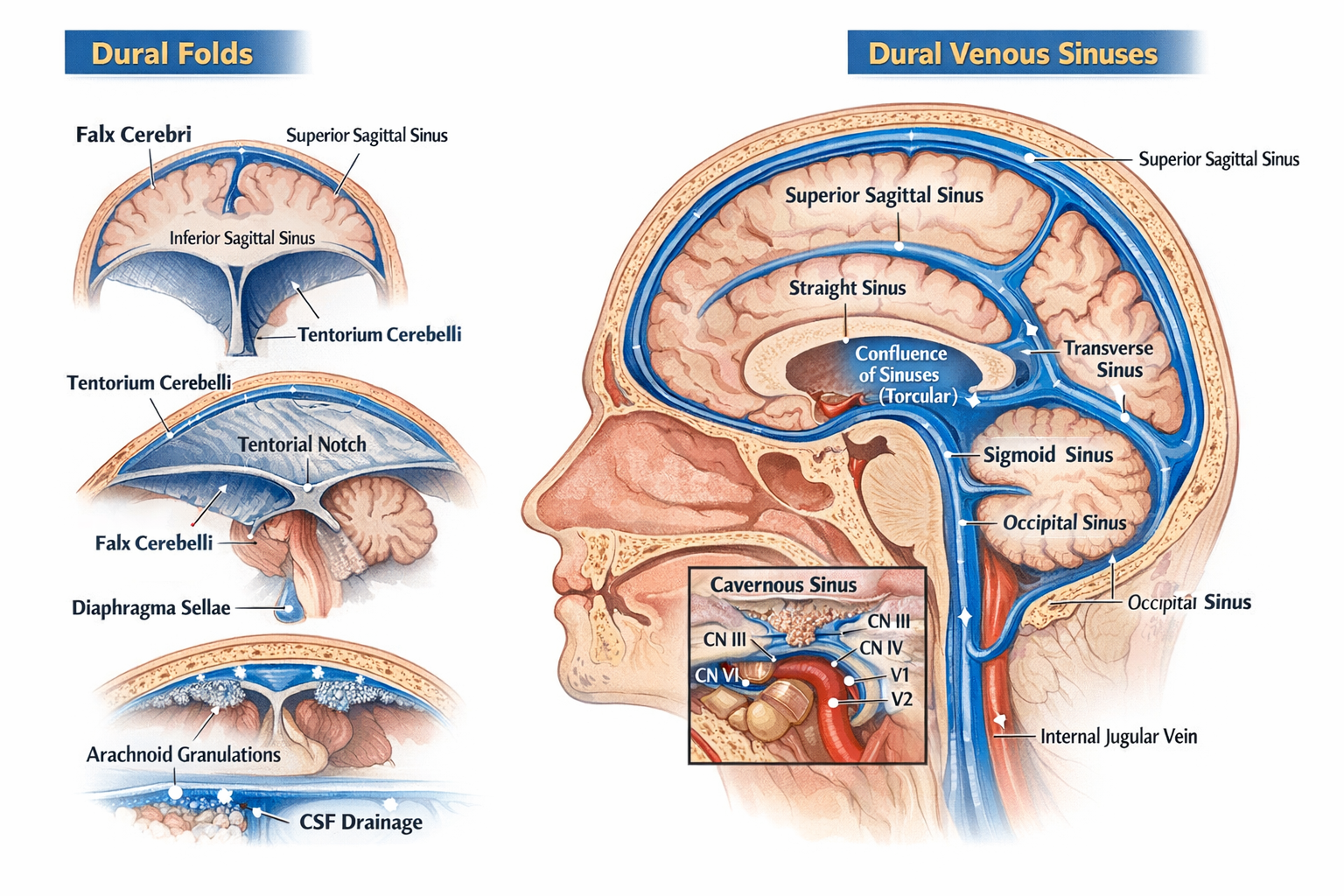
Dural folds are inward reflections of the meningeal layer of dura mater that partition and support the brain within the cranial cavity and help prevent excessive brain movement.
The major dural folds are falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli, falx cerebelli, and diaphragma sellae.
Falx cerebri is a sickle-shaped vertical dural fold that lies in the midline and separates the right and left cerebral hemispheres.
The tentorium cerebelli separates the cerebrum above from the cerebellum below.
The tentorial notch is an opening in the tentorium cerebelli that allows passage of the midbrain; it is clinically important because transtentorial herniation can compress vital brainstem structures.
The diaphragma sellae forms the roof of the sella turcica and covers the pituitary gland, with a central opening for the pituitary stalk.
Dural venous sinuses are endothelial-lined venous channels located between the periosteal and meningeal layers of dura mater that drain venous blood and cerebrospinal fluid from the brain.
The superior sagittal sinus lies in the upper attached margin of the falx cerebri.
The superior sagittal sinus receives cerebrospinal fluid through arachnoid villi and arachnoid granulations.
The cavernous sinus is a paired dural venous sinus located on either side of the body of the sphenoid; it is clinically significant because it contains the internal carotid artery and cranial nerves, making it vulnerable to infections and thrombosis.
The abducent nerve (cranial nerve VI) runs within the cavernous sinus alongside the internal carotid artery.
The confluence of sinuses, also known as torcular Herophili, is the junction where the superior sagittal sinus, straight sinus, and occipital sinus meet.
The sigmoid sinus continues as the internal jugular vein after passing through the jugular foramen.
Dural venous sinuses do not collapse because they have rigid walls formed by dura mater and lack smooth muscle and valves.
MCQ Test - Dural Folds and Dural Venous Sinuses Anatomy, Features and Clinical Significance
No MCQs available for this article.