Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
Anatomy of Spinal Cord Complete Guide Location Structure Tracts Pathways
Frequently Asked Questions
The spinal cord lies within the vertebral canal, extending from the foramen magnum above to the level of L1–L2 vertebrae in adults, where it ends as the conus medullaris.
Adults: Foramen magnum to L1–L2 Newborns: Foramen magnum to L3–L4 The apparent ascent occurs due to differential growth of the vertebral column.
The pia mater is modified to form: Filum terminale Denticulate ligaments Linea splendens These structures stabilize and anchor the spinal cord within the vertebral canal.
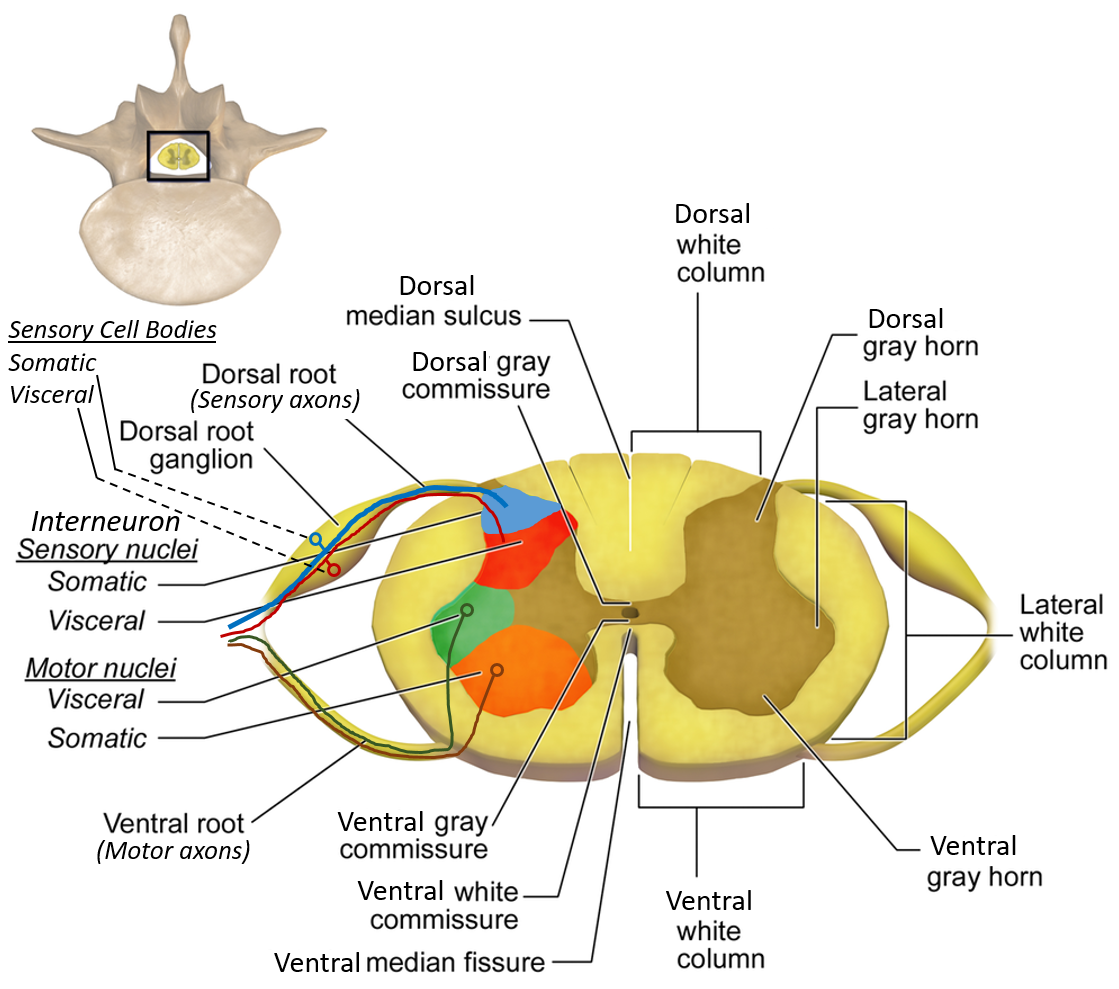
The grey matter is divided into: Anterior horn: Motor neurons Posterior horn: Sensory neurons Lateral horn: Autonomic neurons (T1–L2, S2–S4)
The anterior horn contains lower motor neurons, including: Alpha motor neurons (extrafusal muscle fibers) Gamma motor neurons (muscle spindle regulation)
Important posterior horn nuclei include: Substantia gelatinosa (pain modulation) Nucleus proprius (touch and pressure) Clarke’s column (unconscious proprioception)
UMN lesion: Spastic paralysis, hyperreflexia, Babinski sign LMN lesion: Flaccid paralysis, muscle wasting, fasciculations
The anterior spinothalamic tract carries crude touch and pressure sensations.
MCQ Test - Anatomy of Spinal Cord Complete Guide Location Structure Tracts Pathways
No MCQs available for this article.