Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Neurovascular Structures of the Neck Anatomy Clinical Importance and Exam Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
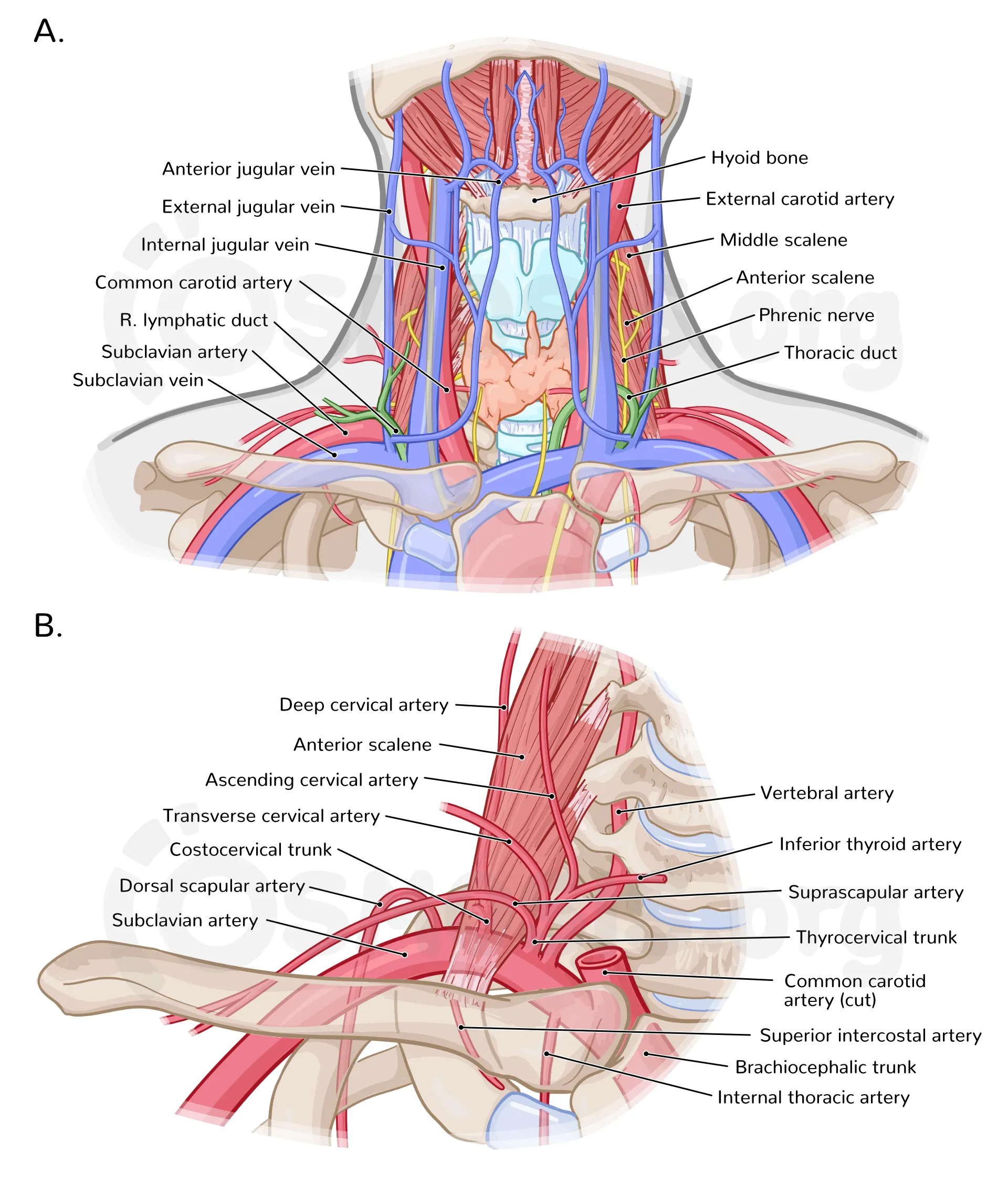
Neurovascular structures of the neck include major arteries veins and nerves such as the common and internal carotid arteries external carotid artery internal and external jugular veins cranial nerves cervical plexus brachial plexus and the cervical sympathetic trunk
The carotid sheath contains the common or internal carotid artery medially the internal jugular vein laterally the vagus nerve posteriorly deep cervical lymph nodes and sympathetic nerve fibers
The common carotid artery bifurcates at the level of the upper border of the thyroid cartilage corresponding to the C4 vertebra
The internal carotid artery supplies the brain and has no branches in the neck
The carotid sinus acts as a baroreceptor and helps regulate blood pressure by sensing changes in arterial wall stretch
The carotid body functions as a chemoreceptor that detects changes in blood oxygen carbon dioxide and pH levels
The vagus nerve lies posteriorly between the carotid artery and internal jugular vein within the carotid sheath
The spinal accessory nerve is commonly injured during posterior triangle surgeries
Injury to the cervical sympathetic trunk can result in Horner syndrome characterized by ptosis miosis and anhidrosis
The phrenic nerve arising from C3 to C5 supplies the diaphragm and passes through the neck
The cervical plexus supplies sensory innervation to the skin of the neck scalp and shoulder region and motor innervation to infrahyoid muscles and the diaphragm via the phrenic nerve
The internal jugular vein is commonly used for central venous catheterization due to its large size and predictable location
Horner syndrome is caused by injury to the cervical sympathetic chain leading to loss of sympathetic innervation to the eye and face
The glossopharyngeal nerve provides taste sensation to the posterior one third of the tongue
The carotid sheath is clinically important because it contains vital neurovascular structures and is involved in procedures such as central venous access carotid endarterectomy and evaluation of neck trauma
MCQ Test - Neurovascular Structures of the Neck Anatomy Clinical Importance and Exam Guide
No MCQs available for this article.