Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Radial Nerve, Dorsal Digital Expansion and Anatomical Snuffbox Anatomy Explained
Frequently Asked Questions
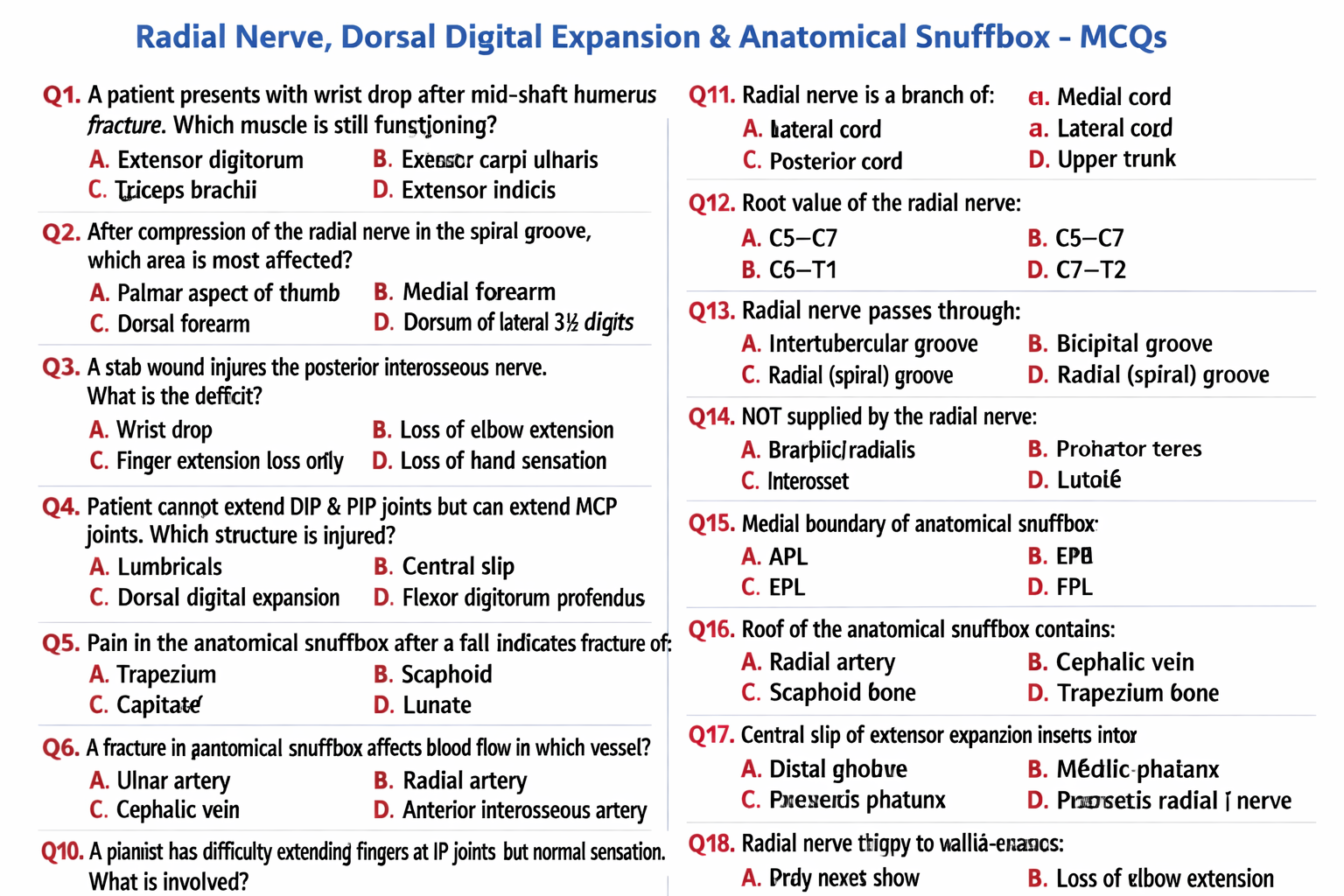
The radial nerve is a terminal branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus with root value C5–T1. It supplies the extensor muscles of the arm and forearm and provides sensory innervation to the posterior upper limb and dorsum of the hand.
The radial nerve is responsible for extension of the elbow, wrist, and fingers, and for sensation over the posterior arm, posterior forearm, and dorsum of the lateral hand.
Wrist drop is the inability to extend the wrist and fingers due to paralysis of extensor muscles following radial nerve injury.
Dorsal digital expansion, also called extensor expansion or extensor hood, is an aponeurotic structure on the dorsum of the fingers formed mainly by the extensor digitorum tendon.
Dorsal digital expansion allows coordinated extension of the interphalangeal joints and enables lumbricals and interossei to flex the metacarpophalangeal joints while extending the interphalangeal joints.
The central slip is a part of the dorsal digital expansion that inserts into the base of the middle phalanx and is essential for extension of the proximal interphalangeal joint.
Boutonnière deformity results from rupture of the central slip of the dorsal digital expansion, leading to flexion of the PIP joint and hyperextension of the DIP joint.
The anatomical snuffbox is a triangular depression on the lateral aspect of the dorsum of the hand that becomes prominent when the thumb is extended.
The lateral boundary is formed by abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis, the medial boundary by extensor pollicis longus, and the proximal boundary by the styloid process of the radius.
The floor of the anatomical snuffbox is formed by the scaphoid and trapezium bones.
The main content of the anatomical snuffbox is the radial artery, while the roof contains the superficial branch of the radial nerve and the cephalic vein.
Tenderness in the anatomical snuffbox is a classic sign of scaphoid fracture, which carries a risk of avascular necrosis due to compromised blood supply.
MCQ Test - Radial Nerve, Dorsal Digital Expansion and Anatomical Snuffbox Anatomy Explained
No MCQs available for this article.