Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Basal Ganglia Anatomy Functions Pathways and Clinical Disorders Explained
Frequently Asked Questions
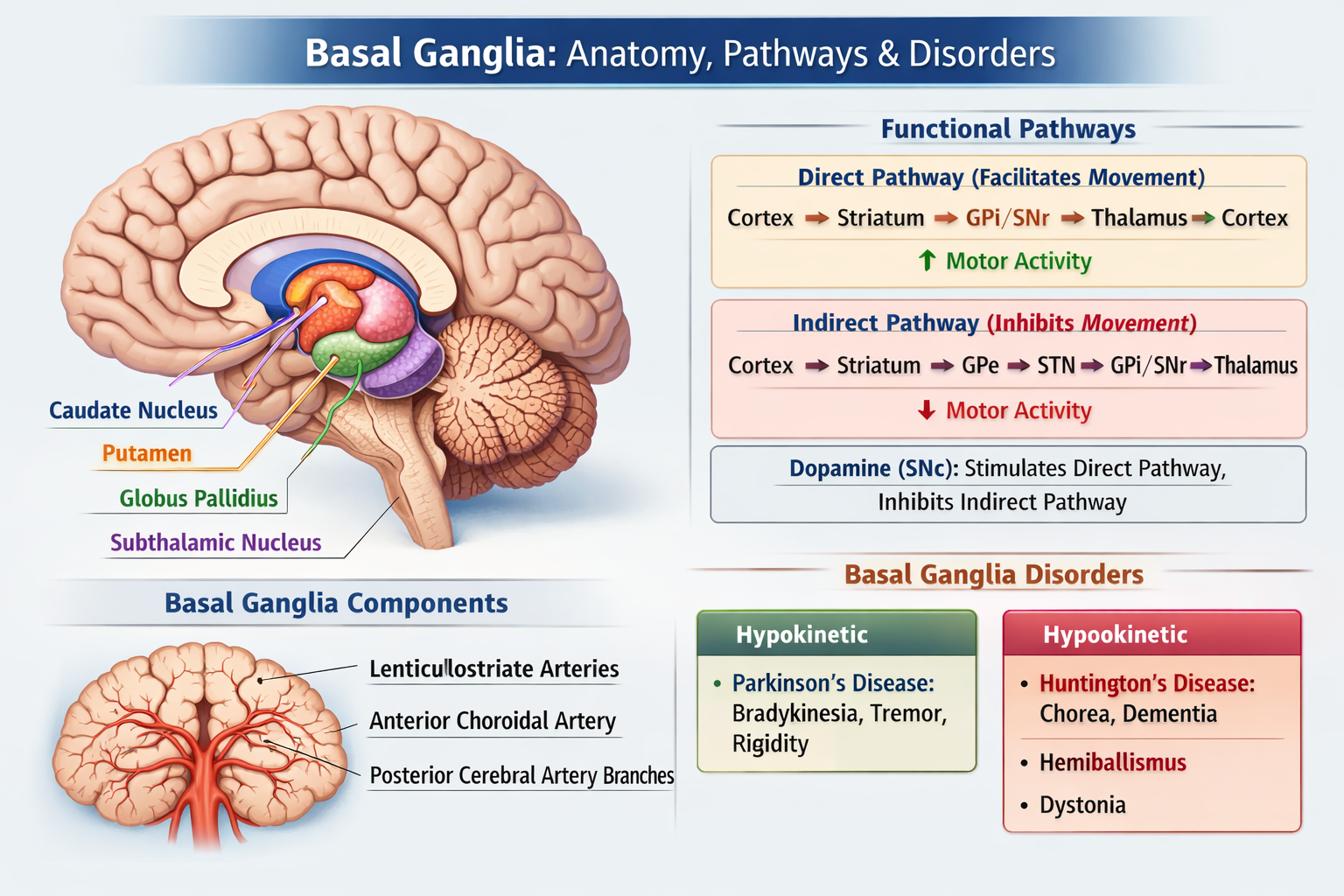
The basal ganglia are a group of deep subcortical nuclei that regulate voluntary movement muscle tone posture procedural learning and certain cognitive and emotional functions.
The basal ganglia include the caudate nucleus putamen globus pallidus subthalamic nucleus and substantia nigra.
The primary function of the basal ganglia is to modulate motor activity by facilitating desired movements and inhibiting unwanted movements.
The direct pathway facilitates movement by reducing inhibitory output to the thalamus while the indirect pathway inhibits movement by increasing thalamic inhibition.
Dopamine from the substantia nigra pars compacta stimulates the direct pathway via D1 receptors and inhibits the indirect pathway via D2 receptors thereby promoting movement.
The basal ganglia are mainly supplied by the lenticulostriate branches of the middle cerebral artery along with contributions from the anterior choroidal artery.
Damage to the basal ganglia results in movement disorders characterized by either reduced movement hypokinetic disorders or excessive involuntary movements hyperkinetic disorders.
Parkinson disease is associated with degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta.
Huntington disease primarily affects the caudate nucleus leading to chorea behavioral changes and cognitive decline.
Hemiballismus is a hyperkinetic movement disorder characterized by violent flinging movements caused by lesions of the subthalamic nucleus.
MCQ Test - Basal Ganglia Anatomy Functions Pathways and Clinical Disorders Explained
No MCQs available for this article.