Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Deep Cervical Fascia and Triangles of the Neck Anatomy Explained in Detail
Frequently Asked Questions
Deep cervical fascia is a dense connective tissue layer of the neck that encloses muscles, blood vessels, nerves, and viscera, providing support, compartmentalization, and a pathway for the spread or limitation of infections.
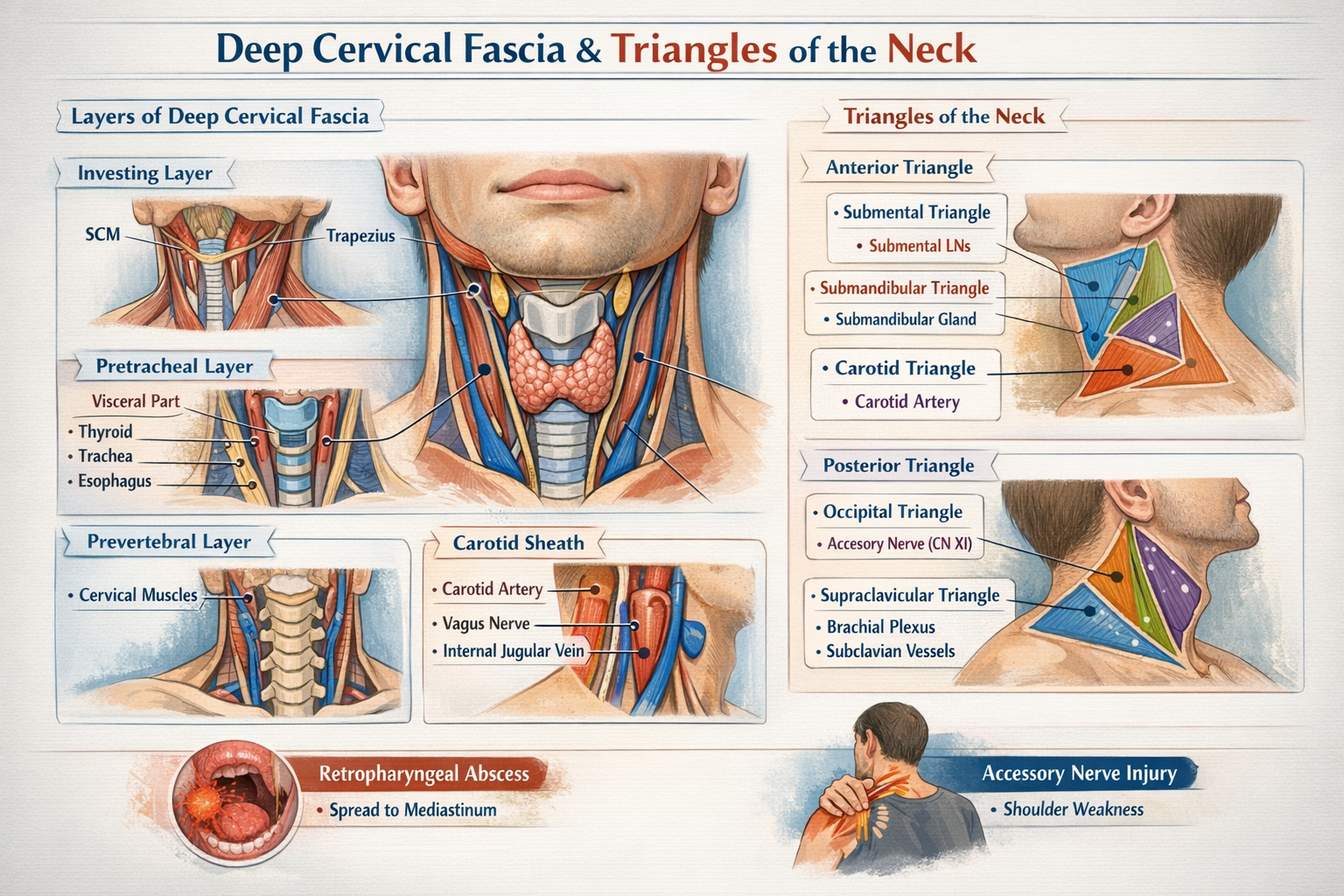
The main layers are the investing layer, pretracheal layer (muscular and visceral parts), prevertebral layer, and the carotid sheath.
The investing layer encloses the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles.
The pretracheal fascia encloses the infrahyoid muscles (muscular part) and the thyroid gland, trachea, and esophagus (visceral part).
The thyroid gland moves during swallowing because it is attached to the larynx and trachea by the visceral part of the pretracheal fascia, especially through Berry’s ligament.
The carotid sheath contains the common and internal carotid artery, internal jugular vein, vagus nerve, deep cervical lymph nodes, and sympathetic fibers.
The prevertebral layer of deep cervical fascia extends laterally to form the axillary sheath enclosing the subclavian artery and brachial plexus.
The retropharyngeal space lies between the buccopharyngeal fascia and alar fascia and is clinically important because infections here can spread to the mediastinum.
The sternocleidomastoid muscle divides the neck into the anterior triangle and the posterior triangle.
The anterior triangle is subdivided into the submental, submandibular (digastric), carotid, and muscular triangles.
The posterior triangle is bounded anteriorly by the sternocleidomastoid, posteriorly by the trapezius, inferiorly by the clavicle, and superiorly at the apex where SCM and trapezius meet.
The spinal accessory nerve (cranial nerve XI) is most vulnerable as it runs superficially across the posterior triangle.
The carotid triangle contains the carotid bifurcation, carotid sinus, and carotid body.
The muscular triangle provides access to the trachea and thyroid gland.
Deep cervical fascia directs the spread of neck infections, supports vital structures, forms fascial spaces, and explains clinical features such as painful parotid swelling and mediastinal spread of infections.
MCQ Test - Deep Cervical Fascia and Triangles of the Neck Anatomy Explained in Detail
No MCQs available for this article.