Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Brugada Syndrome and Sudden Cardiac Death Complete Clinical Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
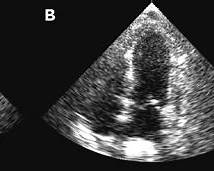
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy is an acute, reversible form of heart failure characterized by transient left ventricular systolic dysfunction, often triggered by intense emotional or physical stress, and mimicking acute coronary syndrome without obstructive coronary artery disease.
Common triggers include emotional stress such as grief or fear, physical stress like sepsis or surgery, neurological events including stroke or subarachnoid hemorrhage, and excessive catecholamine exposure.
Diagnosis is based on clinical presentation, ECG changes, modest troponin elevation, echocardiographic regional wall motion abnormalities beyond a single coronary territory, absence of obstructive coronary disease, and supportive cardiac MRI findings.
Most patients recover left ventricular function within weeks to months, although acute complications such as cardiogenic shock, arrhythmias, and thromboembolism may occur during the initial phase.
Brugada syndrome is an inherited cardiac channelopathy characterized by a distinctive ECG pattern and an increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in individuals with structurally normal hearts.
The diagnostic ECG finding is a type 1 Brugada pattern, defined by coved ST-segment elevation of at least 2 mm in leads V1 and V2 followed by a negative T wave.
Fever exacerbates sodium channel dysfunction, increasing the risk of malignant ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death.
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator implantation is the definitive treatment for patients with prior cardiac arrest, documented ventricular arrhythmias, or high-risk syncope.
Sudden cardiac death is an unexpected death due to cardiac causes occurring within a short time period, usually resulting from ventricular tachyarrhythmias such as ventricular fibrillation.
The most common causes include coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathies, inherited arrhythmia syndromes such as Brugada and long QT syndrome, and acute myocardial infarction.
Ventricular fibrillation is the most common immediate rhythm responsible for sudden cardiac death.
Early cardiopulmonary resuscitation and rapid defibrillation are the most effective interventions for improving survival.
Prevention strategies include optimal medical therapy for underlying heart disease, lifestyle modification, treatment of reversible causes, and implantable cardioverter defibrillator placement in eligible patients.
Although uncommon, Takotsubo cardiomyopathy can lead to sudden cardiac death due to malignant arrhythmias, cardiogenic shock, or mechanical complications during the acute phase.
Genetic testing can identify pathogenic variants such as SCN5A mutations, support family screening, and aid risk assessment, although a negative test does not exclude the diagnosis.