Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
Second Heart Sound S2 Clinical Features Physiology Splitting and Causes
Frequently Asked Questions
The second heart sound S2 is produced by the closure of the semilunar valves, specifically the aortic valve (A2) and pulmonary valve (P2), marking the end of ventricular systole and the beginning of diastole.
S2 is caused by closure of the aortic valve (A2) and the pulmonary valve (P2).
S2 is best heard at the base of the heart, with A2 at the right second intercostal space and P2 at the left second intercostal space.
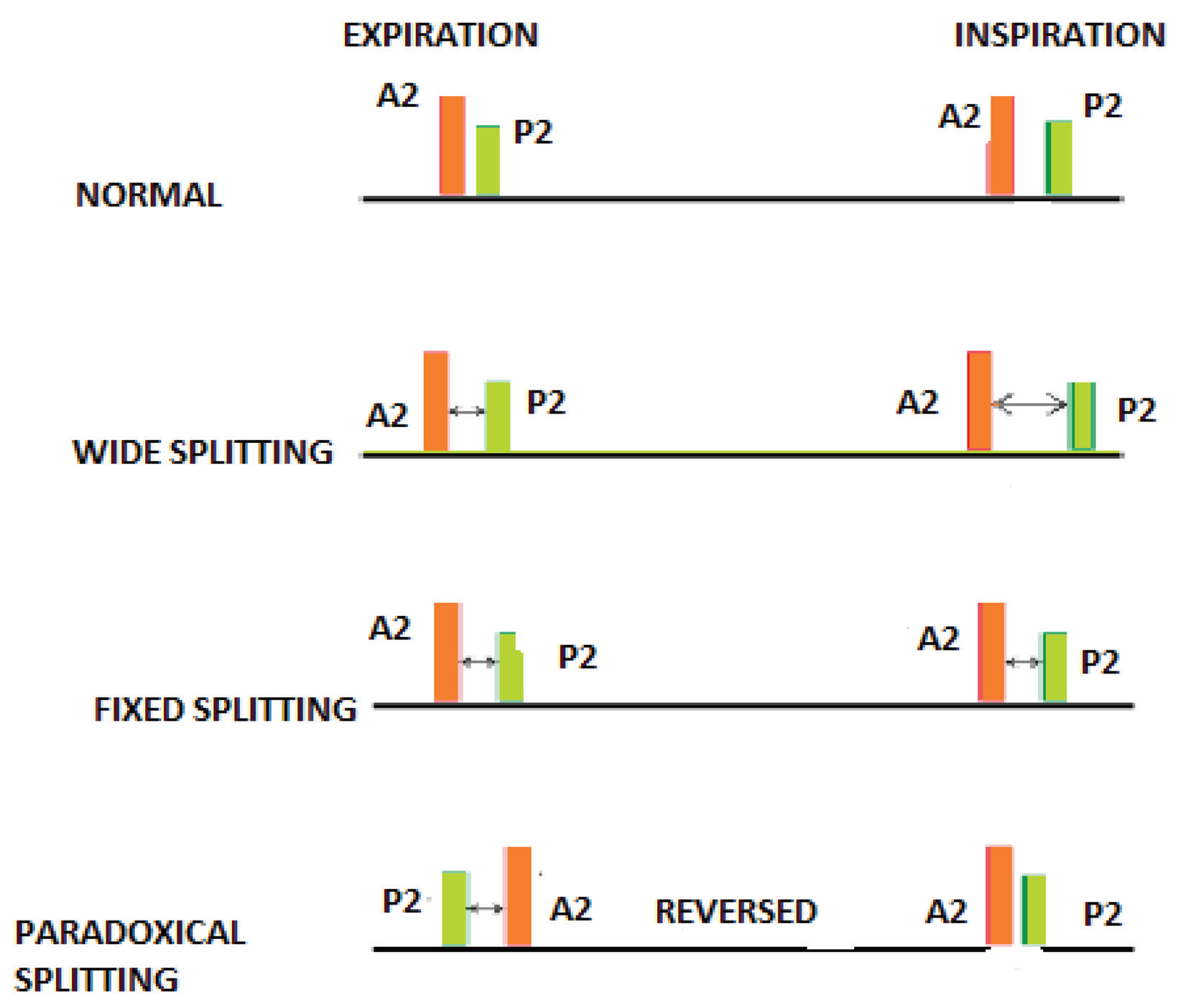
Physiological splitting of S2 refers to normal separation of A2 and P2 during inspiration due to delayed right ventricular emptying and delayed P2.
Wide splitting of S2 occurs due to delayed P2 and is seen in conditions such as right bundle branch block, pulmonary stenosis, and pulmonary embolism.
Fixed splitting of S2 is a constant split during both inspiration and expiration and is classically associated with atrial septal defect.
Paradoxical splitting of S2 occurs when the split is heard during expiration and disappears during inspiration, usually due to delayed A2 as seen in left bundle branch block or severe aortic stenosis.
A loud A2 usually indicates systemic hypertension due to increased force of aortic valve closure.
A soft or absent A2 is seen in severe aortic stenosis and severe aortic regurgitation.
A loud or accentuated P2 is an important clinical sign of pulmonary hypertension.
A soft or absent P2 is commonly caused by pulmonary stenosis due to reduced pulmonary valve closure force.
A single S2 may suggest severe aortic stenosis or severe pulmonary stenosis where one component is absent.
S2 is a high-frequency sound and is best heard using the diaphragm of the stethoscope.
An accentuated and palpable P2 on auscultation is an early and reliable marker of pulmonary hypertension.
During inspiration, increased venous return delays right ventricular emptying, resulting in delayed pulmonary valve closure and splitting of S2.
MCQ Test - Second Heart Sound S2 Clinical Features Physiology Splitting and Causes
No MCQs available for this article.