Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Disorders of Parathyroid Gland Complete Clinical Guide for Medical Students
Frequently Asked Questions
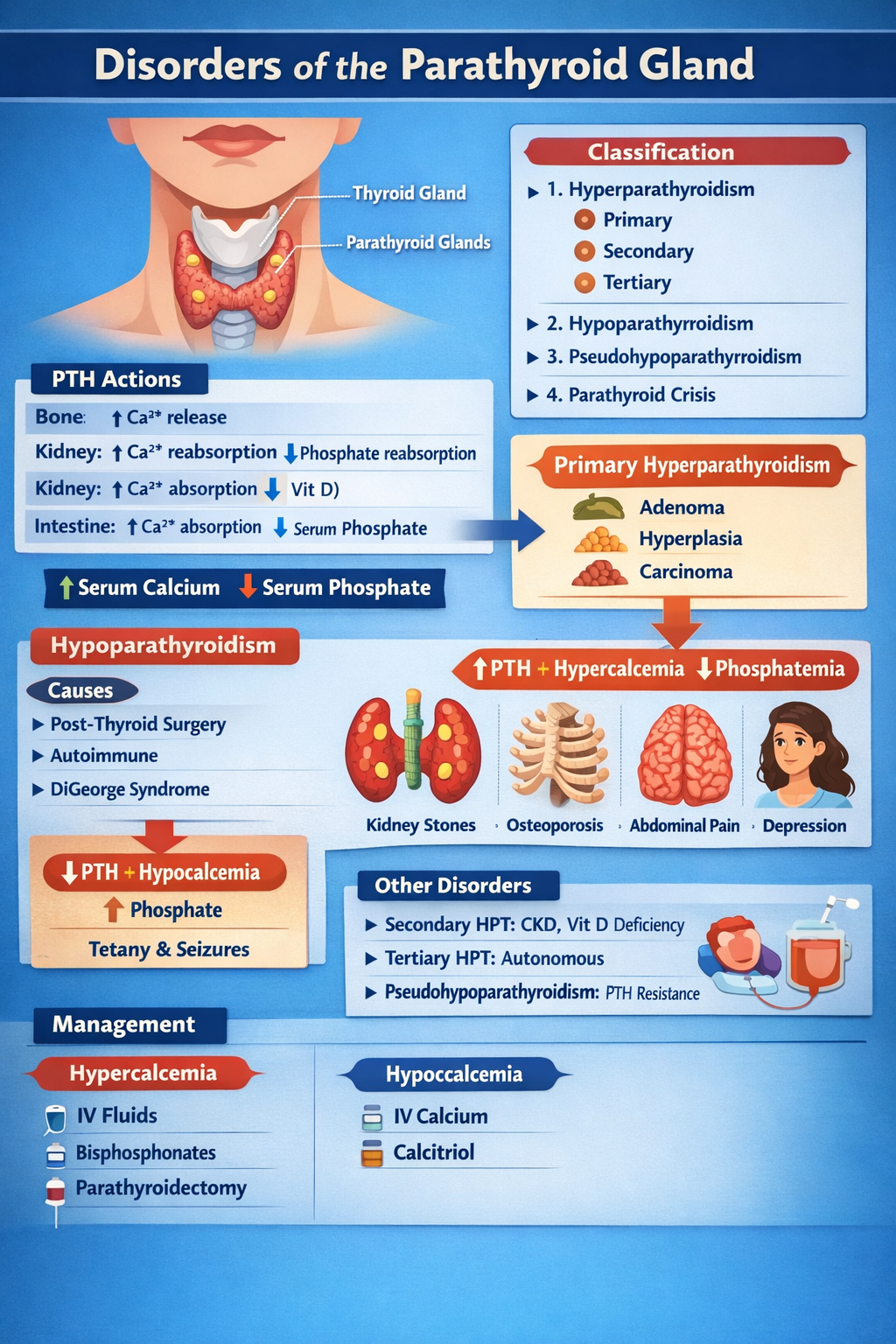
The parathyroid gland regulates calcium and phosphate balance in the body by secreting parathyroid hormone which increases blood calcium levels.
Primary hyperparathyroidism is most commonly caused by a parathyroid adenoma, followed by parathyroid hyperplasia and rarely parathyroid carcinoma.
Secondary hyperparathyroidism occurs due to chronic low calcium levels, most often from chronic kidney disease or vitamin D deficiency.
Tertiary hyperparathyroidism occurs when long-standing secondary hyperparathyroidism leads to autonomous overproduction of parathyroid hormone and hypercalcemia.
Common symptoms include kidney stones, bone pain, muscle weakness, constipation, depression, and excessive urination.
High serum calcium, low serum phosphate, elevated parathyroid hormone, and increased urinary calcium are typical findings.
Hypoparathyroidism is most commonly caused by accidental removal or damage to the parathyroid glands during thyroid or neck surgery.
Signs include muscle cramps, tingling, tetany, seizures, Chvostek sign, Trousseau sign, and prolonged QT interval.
Pseudohypoparathyroidism is a condition in which the body is resistant to parathyroid hormone despite high hormone levels, leading to low calcium and high phosphate.
Treatment depends on the disorder and includes surgery for hyperparathyroidism, calcium and vitamin D supplementation for hypoparathyroidism, and medical therapy for secondary causes.