Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Malpresentation in Pregnancy Causes Types Diagnosis and Management
Frequently Asked Questions
Malpresentation is any fetal presentation other than vertex (head-down, occipito-anterior) at the time of labor, such as breech, transverse lie, face, or brow presentation.
Breech presentation is the most common malpresentation, occurring in about 3–4% of term pregnancies.
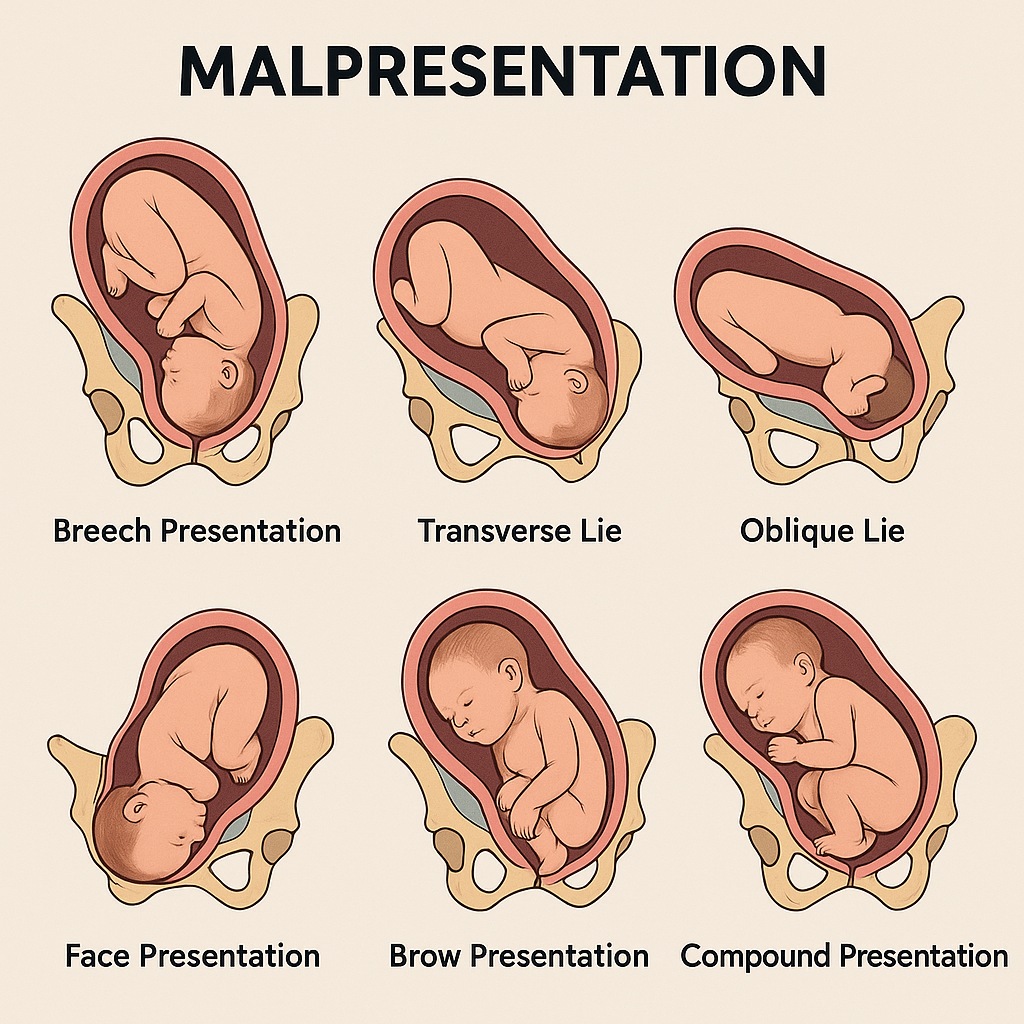
The main types include: Breech presentation Transverse lie Oblique lie Face presentation Brow presentation Compound presentation
Common causes include: Prematurity Placenta previa Uterine anomalies Multiple pregnancy Polyhydramnios Fetal congenital anomalies
Malpresentation is diagnosed by: Abdominal examination (Leopold’s maneuvers) Vaginal examination during labor Ultrasound, which is the most reliable method
Transverse lie is considered the most dangerous malpresentation because vaginal delivery is impossible and there is a high risk of cord prolapse and uterine rupture.
Yes, some malpresentations (especially breech) can be corrected by External Cephalic Version (ECV) after 36–37 weeks, provided there are no contraindications.
Cesarean section is required in: Transverse lie Persistent brow presentation Mentum posterior face presentation Footling breech Malpresentation with fetal distress or CPD