Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Respiratory System Physiology Complete Guide for Medical Students
Frequently Asked Questions
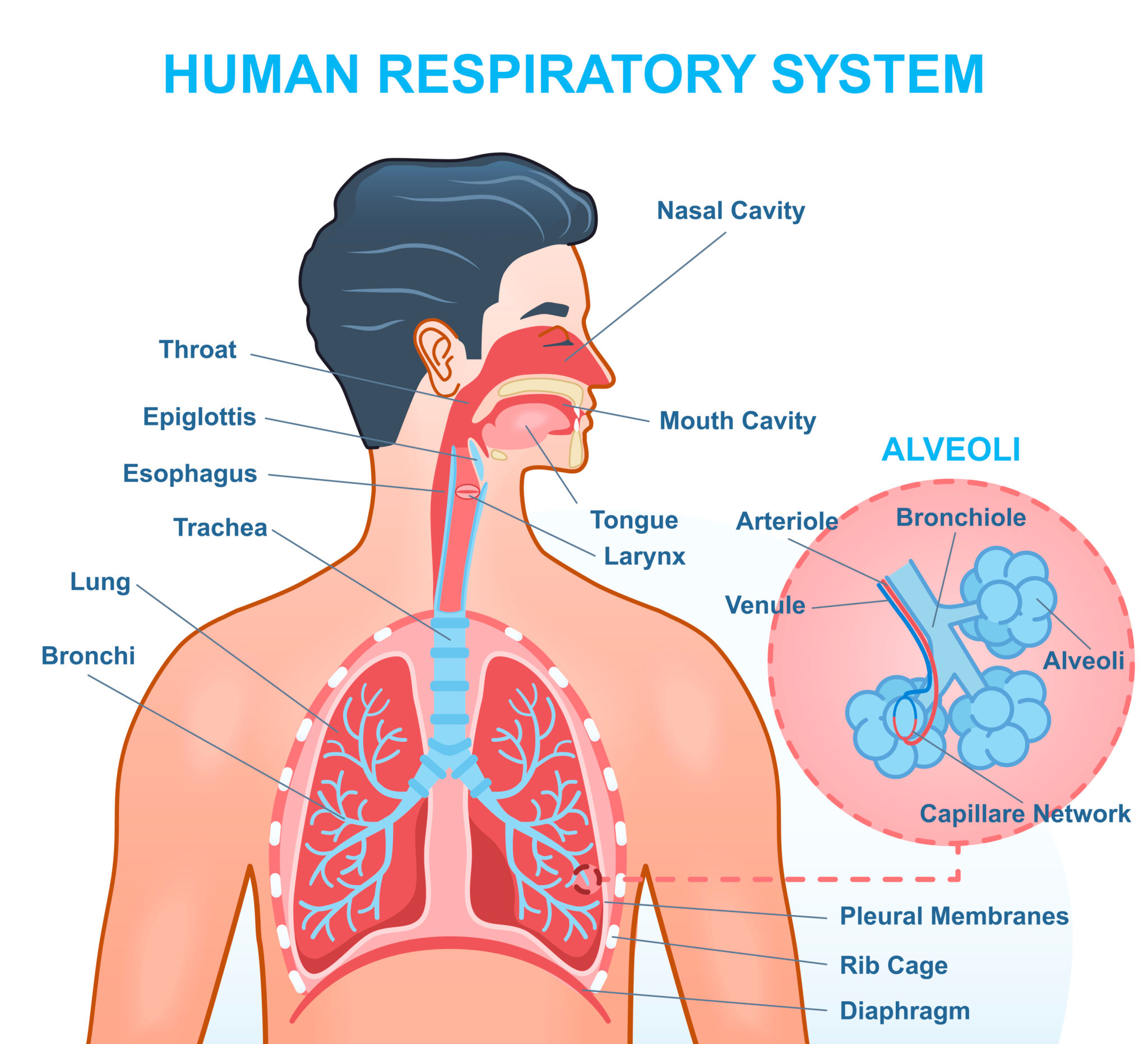
The primary function of the respiratory system is gas exchange, which involves uptake of oxygen into the blood and elimination of carbon dioxide from the body. It also plays a crucial role in acid–base balance, phonation, defense mechanisms, and metabolic functions.
Ventilation refers to the mechanical movement of air into and out of the lungs, while respiration includes ventilation, diffusion of gases across the alveolar membrane, transport of gases in blood, and cellular utilization of oxygen.
Alveolar ventilation is determined by tidal volume, respiratory rate, and dead space. It is calculated as (tidal volume minus dead space) multiplied by respiratory rate and directly influences arterial carbon dioxide levels.
Pulmonary surfactant reduces surface tension within alveoli, preventing alveolar collapse during expiration, increasing lung compliance, and reducing the work of breathing. It is produced by type II pneumocytes.
The ventilation perfusion ratio is the ratio of alveolar ventilation to pulmonary blood flow. A normal value is about 0.8. Matching of ventilation and perfusion is essential for efficient gas exchange, and mismatch leads to hypoxemia.
Physiological shunt is the main cause of hypoxemia that does not correct with oxygen therapy, as blood bypasses ventilated alveoli, commonly seen in pneumonia and pulmonary edema.
Increased carbon dioxide, increased hydrogen ion concentration, increased temperature, and increased 2,3-BPG shift the curve to the right, facilitating oxygen unloading to tissues.
Central chemoreceptors located in the medulla are most sensitive to changes in carbon dioxide via changes in cerebrospinal fluid pH and provide the strongest drive for respiration.
Respiratory acidosis occurs due to hypoventilation leading to carbon dioxide retention, increased PaCO₂, and a fall in blood pH. Renal compensation occurs by increased bicarbonate reabsorption.
Emphysema causes destruction of elastic tissue in the lungs, leading to loss of elastic recoil. This results in airway collapse during expiration and air trapping.