Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Hypertension Clinical Guide Diagnosis Management Complications
Frequently Asked Questions
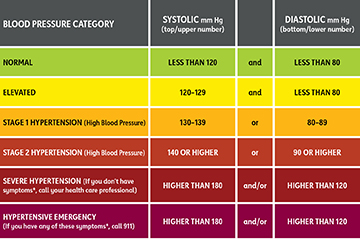
Hypertension is a chronic medical condition characterized by persistently elevated arterial blood pressure, usually defined as systolic BP ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic BP ≥90 mmHg on repeated measurements.
Hypertension is classified into primary (essential) hypertension, which has no identifiable cause, and secondary hypertension, which results from an underlying condition such as renal, endocrine, or vascular disease.
Hypertensive urgency involves severe BP elevation without acute target organ damage, while hypertensive emergency includes severe hypertension with evidence of acute organ damage such as stroke, pulmonary edema, or acute kidney injury.
Most patients are asymptomatic. When present, symptoms may include headache, dizziness, palpitations, blurred vision, chest pain, or shortness of breath, especially in severe hypertension.
Resistant hypertension is blood pressure that remains above target despite the use of three antihypertensive drugs of different classes, including a diuretic, at optimal doses.
Common causes include chronic kidney disease, renal artery stenosis, primary hyperaldosteronism, pheochromocytoma, Cushing syndrome, obstructive sleep apnea, and coarctation of the aorta.
ACE inhibitors reduce intraglomerular pressure, decrease proteinuria, and slow the progression of diabetic nephropathy while effectively controlling blood pressure.
Isolated systolic hypertension is defined as elevated systolic BP (≥140 mmHg) with normal diastolic BP (<90 mmHg), commonly seen in elderly patients due to arterial stiffness.
Lifestyle measures include salt restriction, weight loss, regular physical activity, DASH diet, reduced alcohol intake, smoking cessation, and stress management.
White coat hypertension refers to elevated blood pressure readings in a clinical setting with normal readings outside the clinic, usually confirmed by ambulatory or home BP monitoring.
Masked hypertension occurs when office BP readings are normal but ambulatory or home BP measurements are consistently elevated, carrying a high cardiovascular risk.
Target organ damage includes left ventricular hypertrophy, heart failure, coronary artery disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, hypertensive retinopathy, and peripheral arterial disease.
ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, and direct renin inhibitors are contraindicated in pregnancy due to risk of fetal toxicity.
Ambulatory BP monitoring helps diagnose white coat and masked hypertension, assess BP variability, and predict cardiovascular risk more accurately than office readings.
Abrupt discontinuation of clonidine can cause rebound hypertension due to sudden sympathetic overactivity, which may be severe and life-threatening.
MCQ Test - Hypertension Clinical Guide Diagnosis Management Complications
No MCQs available for this article.