Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
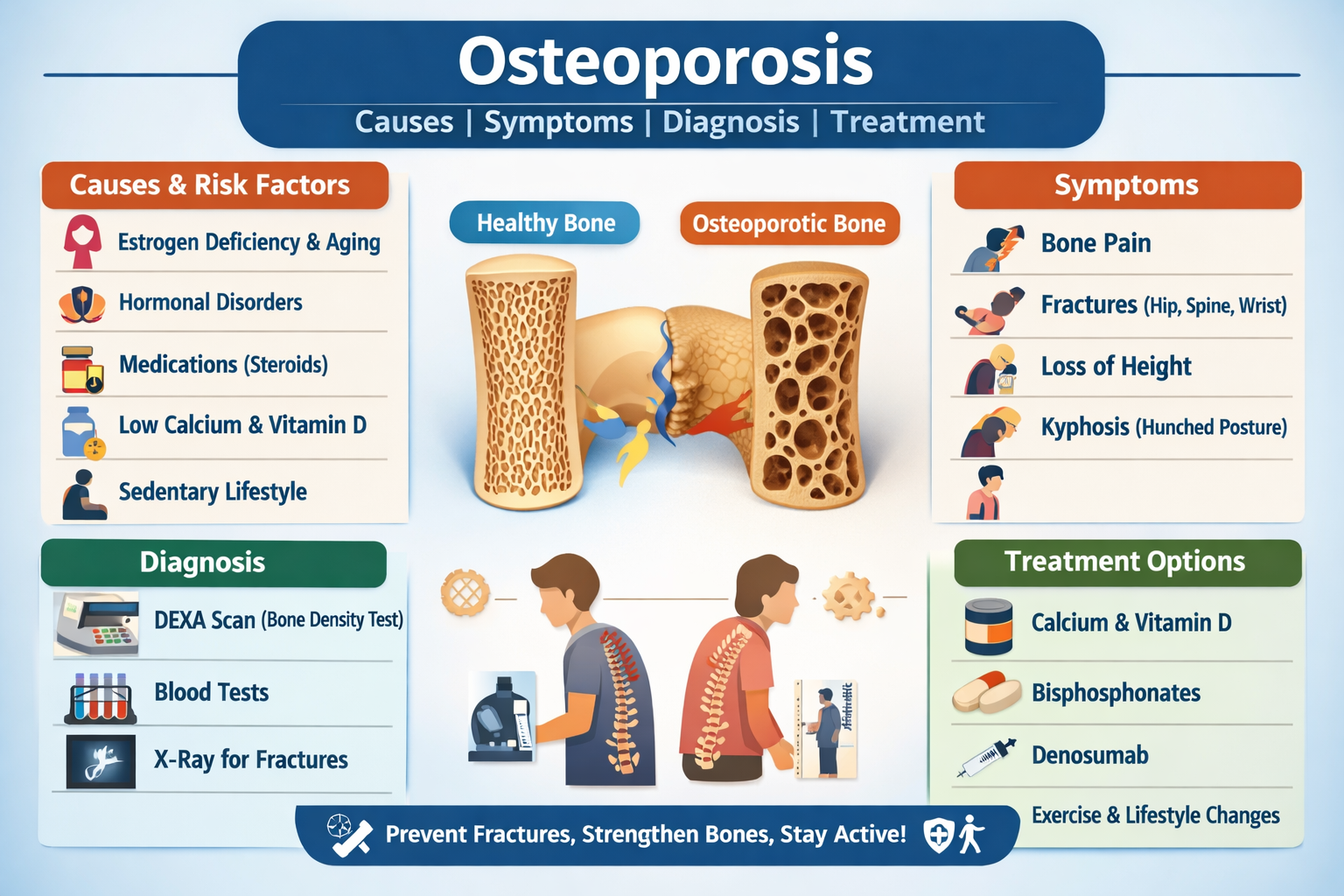
Osteoporosis Causes Symptoms Diagnosis and Treatment Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by decreased bone density and structural weakness, increasing the risk of fractures.
Causes include aging, postmenopausal estrogen deficiency, long-term steroid use, poor calcium and vitamin D intake, sedentary lifestyle, and genetic factors.
Postmenopausal women, elderly individuals, people with low body weight, smokers, chronic steroid users, and those with hormonal disorders are at higher risk.
Osteoporosis is often asymptomatic in early stages until fractures occur; early signs may include mild back pain and gradual height loss.
Common complications include hip fractures, vertebral compression fractures, chronic back pain, spinal deformity, disability, and increased mortality.
The gold standard diagnostic test is a DEXA scan, which measures bone mineral density and provides a T-score.
A T-score of −2.5 or lower confirms the diagnosis of osteoporosis.
Regular weight-bearing exercise, adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, smoking cessation, limiting alcohol, and fall prevention strategies help prevent osteoporosis.
Bisphosphonates such as alendronate are the first-line pharmacologic treatment to reduce bone resorption and fracture risk.
Alternatives include denosumab, raloxifene, teriparatide, and hormone replacement therapy depending on patient profile.
Vitamin D improves calcium absorption and supports bone mineralization, reducing bone loss.
A fragility fracture is a bone fracture that occurs after minor trauma due to weakened osteoporotic bones.
Bone loss cannot be fully reversed, but treatment can significantly improve bone density and reduce fracture risk.
DEXA scanning is usually recommended every 1–2 years in high-risk individuals or those on treatment.
A diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, protein, leafy greens, dairy products, and fortified foods supports bone health.
Yes, men can develop osteoporosis, especially with aging, hypogonadism, alcohol use, or long-term medication use.
Long-term corticosteroids, anticonvulsants, heparin, aromatase inhibitors, and excessive thyroid hormone increase osteoporosis risk.
Teriparatide stimulates osteoblast activity, promoting new bone formation and improving bone strength.
Sudden back pain, height loss, spinal curvature, hip pain after minor falls, and reduced mobility are warning signs.
Home safety modifications, balance training, vision correction, proper footwear, and strength exercises reduce fall risk.